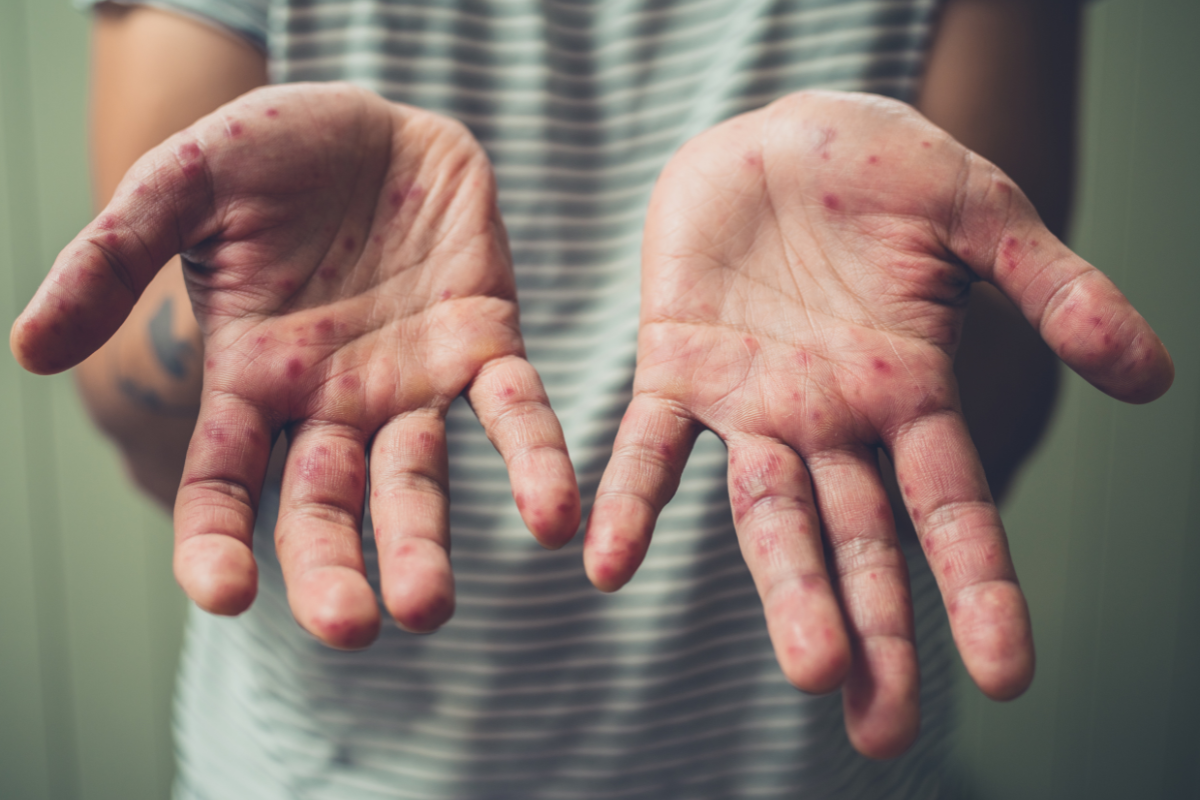
Health authorities in the Philippines have reported a rise in cases of hand, foot, and mouth disease (HFMD) across several regions, prompting calls for heightened vigilance and preventive measures. The Department of Health has indicated that the uptick in infections may be attributed to seasonal trends, which often see an increase in viral illnesses during certain periods each year.
HFMD, primarily affecting children under the age of five, is characterized by fever, mouth sores, and rashes on the hands and feet. While the disease is typically mild and self-limiting, public health officials emphasize the importance of maintaining good hygiene practices to prevent its spread.
In response to the recent surge, health officials are launching awareness campaigns aimed at educating parents and caregivers about the symptoms of HFMD and the necessary precautions to take. These initiatives are crucial for reducing transmission rates and safeguarding the health of young children.
As the situation evolves, the Department of Health is committed to monitoring case trends and implementing measures to mitigate the impact of HFMD within communities. The emphasis on hygiene and education serves as a cornerstone of public health efforts to combat this and other communicable diseases.